Last week, we shared the key highlights and release plan for GreptimeDB v1.0.
This week, as scheduled, we’re thrilled to announce the first beta release — v1.0.0-beta.1!
This release marks a major milestone on our path to the v1.0 GA, bringing us closer to a production-ready, stable GreptimeDB.
Development Statistics
Here’s a snapshot of what went into this release:
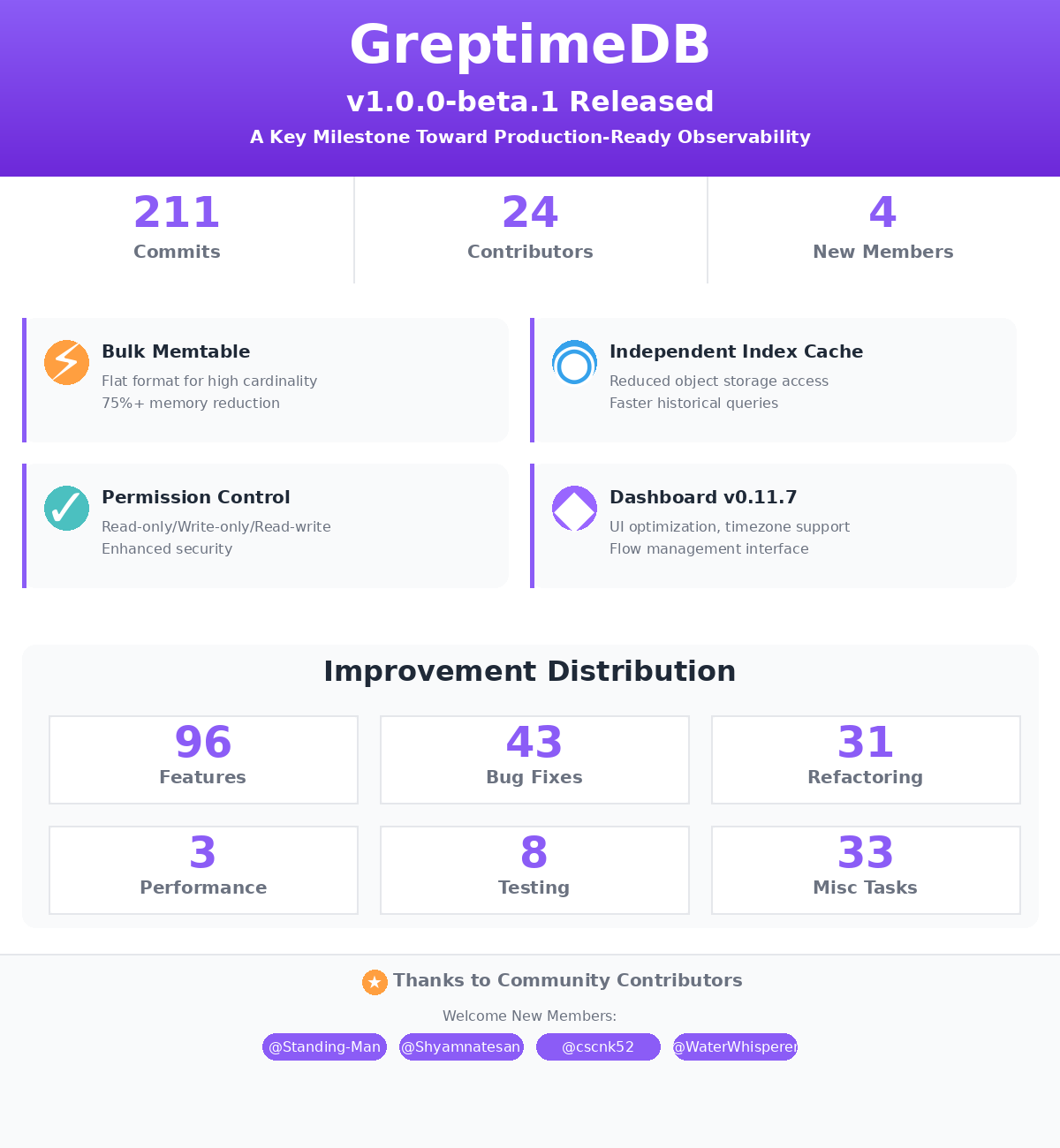
- 211 commits merged into the main branch
- 24 contributors participated
- 4 new contributors joined the project for the first time:
- @Standing-Man
- @Shyamnatesan
- @cscnk52
- @WaterWhisperer
Highlights across all changes
- 96 enhancements: Introduced the experimental flat format for significantly faster queries, and optimized async index building for better write throughput.
- 43 bug fixes: Addressed PromQL timestamp and column reference issues, fixed crashes and concurrency limits with the flat format, improved region migration and failure detection, and resolved alias query problems.
- 31 refactors: Unified UDF implementation to align with DataFusion’s design, simplified function traits, and improved test configuration and infrastructure.
- 3 performance boosts: Bulk Memtable now delivers higher write throughput and reduces memory usage; optimized Arrow-to-protocol conversions; and improved Jaeger API query performance.
- 8 testing improvements: Expanded flat-format test coverage, improved upgrade compatibility, and enhanced deletion/filtering tests.
- 33 misc updates: Migrated to Rust 2024 edition, upgraded DataFusion to v50, and enhanced developer tools, workflows, and monitoring metrics.
👏 Huge thanks to all 24 contributors, and a warm welcome to the 4 new members of our community!
If you’re interested in observability databases and time-series tech, come join us — the more, the merrier!
Feature Highlights
Dashboard v0.11.7
- Metrics UI: Table and chart views are now in separate tabs; instant and range queries split; added time picker and multi-value display.
- Timezone handling: Added timezone validation and local storage persistence.
- Flow management: Added an intuitive UI for Flow task CRUD operations.
Bulk Memtable & Flat Format
This beta introduces Bulk Memtable and the new flat format, designed to work together for high-cardinality primary-key scenarios.
Bulk Memtable drastically reduces memory usage when ingesting huge numbers of unique keys — when primary key cardinality exceeds ~2 million, memory usage can drop by over 75%.
It performs best with larger write batches (we recommend ≥ 1024 rows per batch).
The flat format also boosts query performance over the old storage layout.
Enable both when creating a table:
CREATE TABLE flat_format_table(
request_id STRING,
content STRING,
greptime_timestamp TIMESTAMP TIME INDEX,
PRIMARY KEY (request_id))
WITH ('sst_format' = 'flat');To migrate an existing table:
ALTER TABLE old_format_table
SET 'sst_format' = 'flat';Once converted, tables can’t revert to the old format.
The flat format will gradually become the default in upcoming versions.
Independent Index File Caching
GreptimeDB now caches index files locally on disk. This reduces object-storage I/O during index queries and speeds up historical reads.
By default, 20% of disk-cache space (Write Cache) is reserved for index files — configurable via index_cache_percent.
Unlike previous versions, where only new SSTs benefited from local caching, v1.0.0-beta.1 proactively loads existing index files from object storage in the background on startup, reducing query latency on historical data.
Read-Write Permission Modes
We’ve added permission control for the static user provider, enabling clear read/write access rules.
Supported modes:
rw— read-write (default, backward compatible)ro— read-onlywo— write-only
Configuration example:
# Default: read-write
greptime_user=greptime_pwd
# Explicit forms
greptime_user:rw=greptime_pwd
greptime_user:ro=greptime_pwd
greptime_user:wo=greptime_pwdUsers without explicit permission modes default to read-write, ensuring full compatibility with previous setups.
TQL Value Aliases
TQL now supports AS aliases, making query results cleaner and easier to integrate with SQL tools.
TQL EVAL (0, 30, '10s') http_requests_total AS requests;New objbench Subcommand (Datanode)
We introduced a new benchmarking tool for object storage:
greptime datanode objbench --config datanode.toml --source <path>.parquetIt runs read/write performance tests on SST files and helps diagnose storage or I/O bottlenecks.
Features:
- Run targeted SST performance tests
- Verbose output (
-v/--verbose) - Generate flame graphs (
--pprof-file) - Load full datanode config (
--config)
Example with flamegraph output:
greptime datanode objbench \
--config datanode.toml \
--source <path>.parquet \
--pprof-file flamegraph.svgCompatibility Notes
Jaeger Header Removal
The header x-greptime-jaeger-time-range-for-operations has been removed.
If you’ve used it in your data source or proxy configuration, please update accordingly.
Metric Engine: Sparse Primary-Key Encoding by Default
The Metric Engine now enables sparse primary-key encoding by default for better storage efficiency and query performance.
No data format compatibility issues are introduced.
To revert, explicitly disable sparse encoding in your config:
[metric_engine]
sparse_primary_key_encoding = false # true by defaultThe older option experimental_sparse_primary_key_encoding is deprecated.
greptime_identity JSON Parsing Changes
The greptime_identity pipeline now flattens nested JSON automatically:
- Nested objects become dot-separated keys (
object.a,object.b) - Arrays are stored as JSON strings
- Parameter
flatten_json_objecthas been removed - New option
max_nested_levels(default = 10) controls flattening depth - Beyond that depth, remaining nested data is serialized as JSON strings
This standardizes JSON ingestion and simplifies schema management.
You may need to adjust pipeline configs if you relied on previous behavior.
Closing Thoughts
Read the full release notes on GitHub:
👉 GreptimeDB v1.0.0-beta.1
Many thanks to every contributor and user for your continued support.
We’ll keep moving steadily toward the v1.0 GA, delivering a more robust and enjoyable GreptimeDB experience.