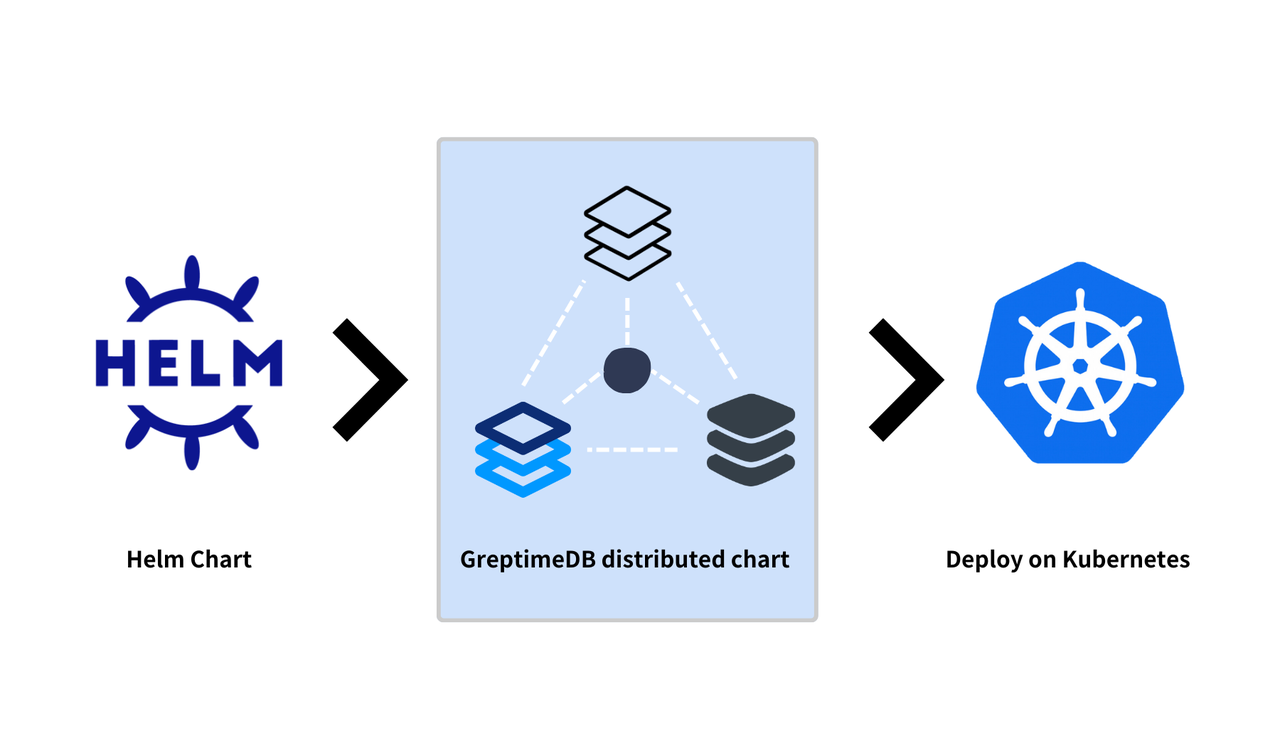
GreptimeDB as a time-series database for the cloud era, has embraced cloud-native technology from day one. Deploying databases on Kubernetes offers scalability, self-healing, and simplified deployment and management, thereby providing robust elasticity and reliability for applications.
Helm is a package manager for managing Kubernetes applications. By using Helm Charts, applications can be easily packaged, configured, and deployed to Kubernetes clusters.
This article explains how to deploy distributed GreptimeDB using Helm Chart and store data on object storage such as AWS S3. Of course, you can also deploy standalone GreptimeDB, navigate to this article to learn more.
Configure the Helm Chart Environment
First, you need to install the Helm tool, which can be done following the instructions in the installation document.
Before deploying the application, add the greptime repository to Helm, which contains a series of available Helm Charts.
Use the following commands to add the greptime repository to Helm:
helm repo add greptime https://greptimeteam.github.io/helm-charts/
helm repo updateUse the following commands to view the greptime Helm Charts available:
helm search repo greptime --devel -lInstall Charts
2.1 Install etcd
helm install etcd oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/etcd \
--set replicaCount=1 \
--set auth.rbac.create=false \
--set auth.rbac.token.enabled=false \
-n default2.2 Install greptimedb-operator
helm install mycluster greptime/greptimedb-cluster -n default2.3 Install greptimedb-cluster
helm install mycluster greptime/greptimedb-cluster -n defaultTo install a specific version of the chart, use:
helm install mycluster greptime/greptimedb-cluster -n default --version <chart-version>View the pods installed using the kubectl command line tool:
kubectl get po -n default
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
etcd-0 1/1 Running 0 2m18s
greptimedb-operator-546b5f9656-tz9gn 1/1 Running 0 2m1s
mycluster-datanode-0 1/1 Running 0 32s
mycluster-datanode-1 1/1 Running 0 27s
mycluster-datanode-2 1/1 Running 0 21s
mycluster-frontend-76cbf55687-4drvx 1/1 Running 0 15s
mycluster-meta-6b7974464b-bbt4h 1/1 Running 0 33s2.4 Unload greptimedb-cluster
helm uninstall mycluster -n defaultStore Data on AWS S3
In a previous tutorial, we shared how to run the GreptimeDB binary and save data to AWS S3. Similarly, we can also deploy GreptimeDB in a containerized manner and store data in the cloud, achieving greater elasticity and reliability.
The detailed steps are as follows:
helm install mycluster greptime/greptimedb-cluster \
--set objectStorage.s3.bucket="your-bucket" \
--set objectStorage.s3.region="region-of-bucket" \
--set objectStorage.s3.root="root-directory-of-data" \
--set objectStorage.credentials.secretName="s3-credentials" \
--set objectStorage.credentials.accessKeyId="your-access-key-id" \
--set objectStorage.credentials.secretAccessKey="your-secret-access-key" \
-n defaultYou can adjust the parameters to your S3 information:
- bucket: S3 Bucket Name
- region: S3 Bucket Region
- root: Data storage directory, set here as
/greptimedb-data - secretName: S3 Credentials Secret Name
- accessKeyId: AWS Access Key ID
- secretAccessKey: AWS Secret Access Key
After the pod starts running, perform a test to write data into S3:
kubectl port-forward -n default svc/mycluster-frontend 4002:4002 > a.out &Connect to GreptimeDB using MySQL protocol:
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -P 4002Execute the create table statement. Here the table name is s3_test_table:
CREATE TABLE s3_test_table (
host STRING,
idc STRING,
cpu_util DOUBLE,
memory_util DOUBLE,
disk_util DOUBLE,
ts TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY(host, idc),
TIME INDEX(ts)
);Insert data into s3_test_table:
INSERT INTO s3_test_table
VALUES
("host1", "idc_a", 11.8, 10.3, 10.3, 1667446797450),
("host1", "idc_a", 80.1, 70.3, 90.0, 1667446797550),
("host1", "idc_b", 50.0, 66.7, 40.6, 1667446797650),
("host1", "idc_b", 51.0, 66.5, 39.6, 1667446797750),
("host1", "idc_b", 52.0, 66.9, 70.6, 1667446797850),
("host1", "idc_b", 53.0, 63.0, 50.6, 1667446797950),
("host1", "idc_b", 78.0, 66.7, 20.6, 1667446798050),
("host1", "idc_b", 68.0, 63.9, 50.6, 1667446798150),
("host1", "idc_b", 90.0, 39.9, 60.6, 1667446798250);You can now log into the AWS S3 console to view the data that has been inserted:
You can also access GreptimeDB through the Dashboard:
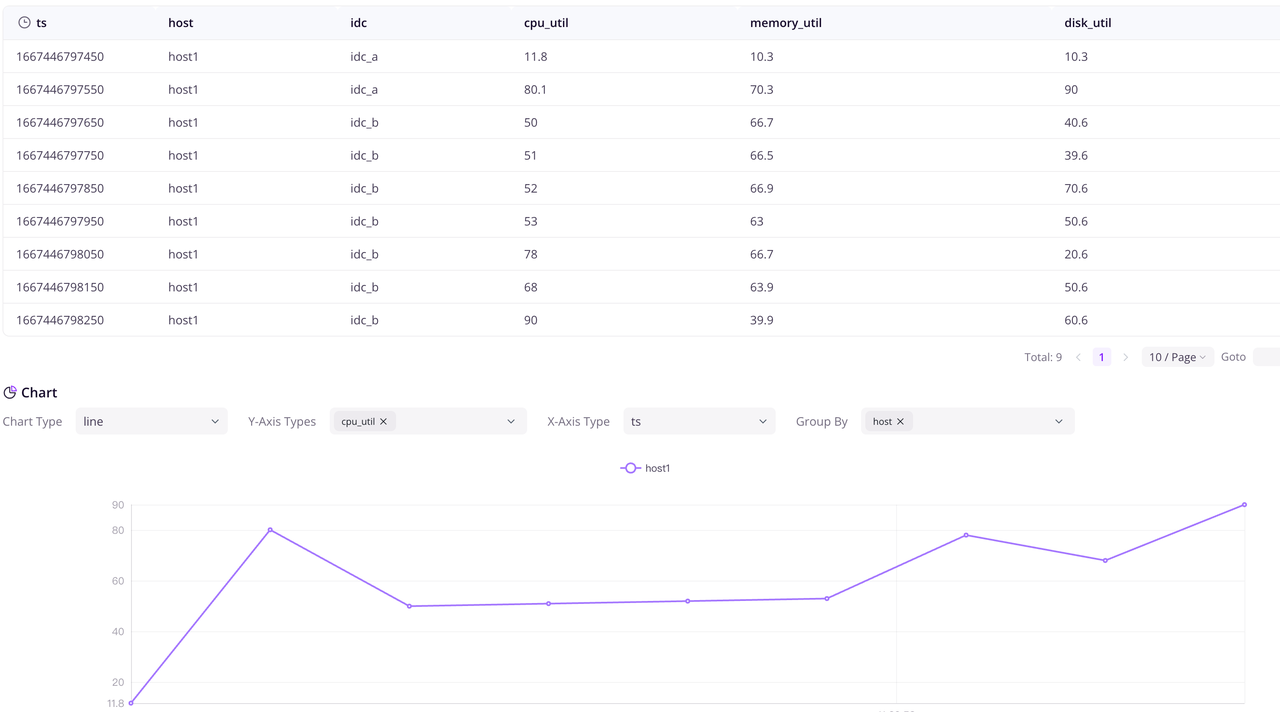
kubectl port-forward -n default svc/mycluster-frontend 4000:4000 > a.out &Visit http://localhost:4000/dashboard/query in your browser to view the Dashboard, and execute select * from s3_test_table; to view the data that has been written.
Unload greptimedb-cluster:
helm uninstall mycluster -n defaultSummary
This article has provided a comprehensive guide on deploying distributed GreptimeDB using Helm Chart, with a focus on configuring data storage solutions using AWS S3. This approach, particularly relevant in the cloud-native era, significantly enhances the flexibility and reliability of data management while streamlining both deployment and management processes.